Cell Structure and Function
Cell theory
- All living things are made up of cells.
- Cells are the smallest working units of all living things.
- All cells come from pre-existing cells through cell division.
Definition of cell
A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions.
Examples
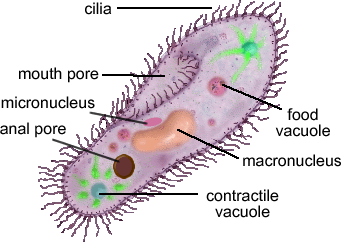
- Amoeba
- Plant stem
- bacteria
- Prokaryotic
- Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic
- Do not have organelles (specialised structures in cells) surrounded by membranes
- Few internal structures
- one-celled organisms e.g. bacteria
Eukaryotic
- Contain organelles surrounded by membranes
- Most living organisms e.g. plant, animal, fungi
- Most commonly found in plant cells&bacteria
- Surrounds the cell membrane
- Rigid structure that maintains the shape, supports & protects cells
- Permeable to small molecules and small proteins only
Membrane
- Selectively/partial* permeable membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell.
Nucleus
- Contain chromatins that control cell activities
- Chromatin contain DNA which is the genetic material
- DNA contain instructions for traits & characteristics and to carry out the cell's function
- Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane
Cytoplasm
- Gel-like mixture
- Surrounded by cell membrane
- Contains organelles
Mitochondria
- Referred to as the "powerhouse" of the cell.
- The food we eat is transformed into energy (ATP) for the cell and our bodies.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
- An interconnected network of tubs and vesicles
- Synthesis of(Make) proteins, fats, steroid
- Transports materials around in cell
- Smooth type: lacks ribosomes
- Rough type (in picture): ribosomes e bedded in surface
Ribosomes
- Each cell contains thousands
- Make proteins
- Found on endoplasmic reticulum & floating throughout the cell
- Why on endoplasmic reticulum? Once the ribosomes make the protein, the protein will go into the endoplasmic reticulum. Endoplasmic reticulum folds the proteins into the correct shape so that the proteins can function properly.
Golgi Apparatus(whole stack)/Golgi Bodies(smaller)
- Works closely with the ER Primary function is to process and package complex molecules such as proteins and fats that are made by cell
- Brings these products to the surface of the cell where they can be secreted
- Other secretions include hormones, antibodies and enzymes.
Lysosome
- Contain digestive enzymes
- Digest excess or worn-out organelles, food particles and engulf bacteria or viruses
- Also help repair worn-out plasma membrane
- They also provide sugars, amino acids and bases which are the foundations of macromolecules
- Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes
Vacuoles
- Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion and waste removal
- Central large vacuole-help plant cells maintain shape
- Food vacuole: formed by phagocytosis (when the cell tries to engulf something.
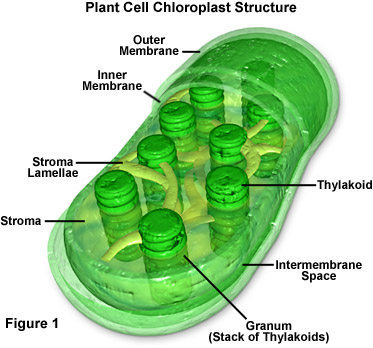
Chloroplast
- Usually found in plant cells (some bacterias have chloroplast too)
- Contains green chlorophyll
- Where photosynthesis takes place
- Converts light energy into chemical energy in glucose.